ustralian AIDS Association *
A project by Ivanhoe Grammar School students Patrick Moio, Imogen Money, Thomas Gazis, Elizabeth Simcevski and Angeline Koutsoukos
*this is not a real organisation


Diagnosis and Testing
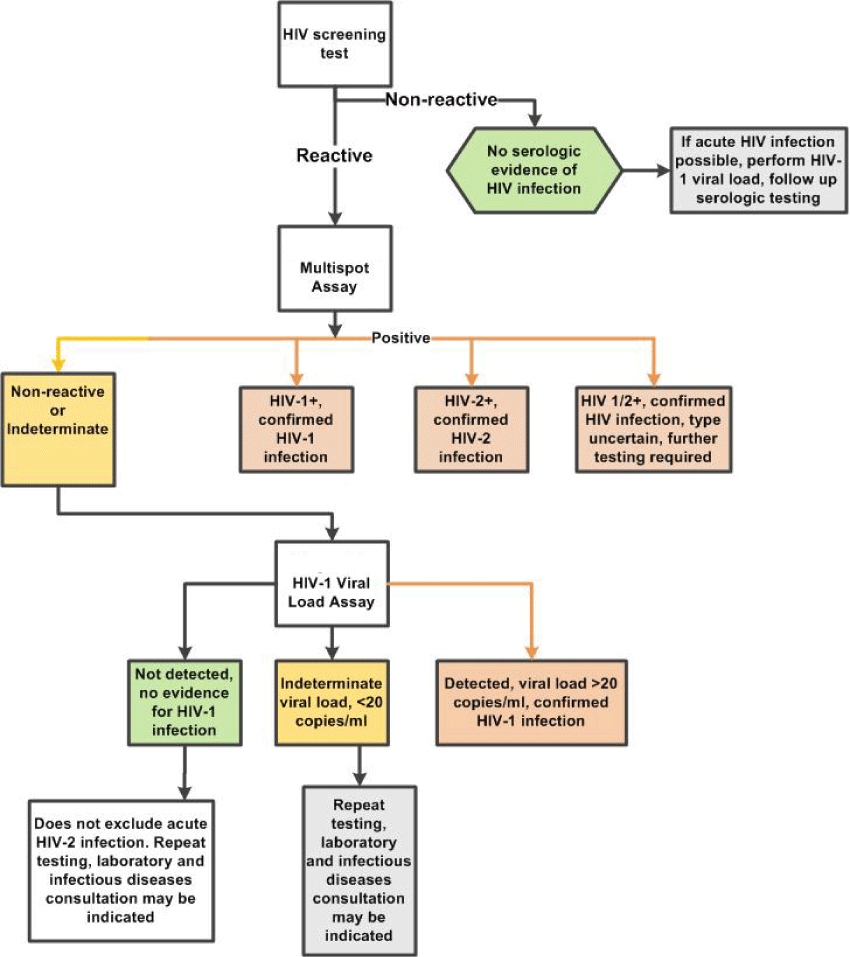
HIV Diagnosis:
To be diagnosed as HIV positive, two HIV tests must come back positive for HIV antibodies. Firstly, an enzyme immunoassay test is taken and then west blot test for confirmation. When a person is confirmed to be HIV positive, they can expect to always have HIV infected cells in their body for the rest of their lives.
From here, it can be passed onto their unborn or born babies through breast feeding or onto their sexual partners. If the virus is left untreated or ignored for too long and progresses into AIDS, it can become life threatening. With our constantly progressing scientific knowledge and technology we have learnt and discovered how to keep this pandemic under control.
AIDS Diagnosis:
AIDS is the most fatal and complex stage of the HIV virus. HIV will not progress into AIDS unless the patient has gone untreated. For a person to be officially diagnosed with AIDS, their CD4 cell count must be below 200. If a person is AIDS infected and has not taken any antiretrovirals, the consequence can potentially be death.
FURTHER EXPLANATION:
Initial Human Immunodifiency Virus (HIV)
infection:
-
400-1,000 T-cells
-
Symtomless
-
Little or no damage to the immune system or other parts of the body
Symptomatic HIV Disease (2-4 weeks after infection):
-
400 to 200 T-cells.
-
Some symptoms
-
At least some damage to the immune system
Autoimmune Deficiancy Syndrome (AIDS):
-
400 to 0 T-cells.
-
Severe symptoms
-
Serious damage to the immune system and other parts of the body

HIV Antibody Test